

Shoulder impingement is an irritation or inflammation of the lubrication sac, the bursa, located just over the rotator cuff and/or inflammation of the rotator cuff tendons, called tendonitis.
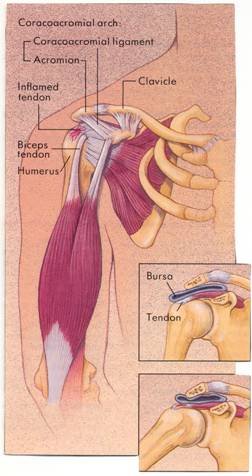
How does it occur? The bursa and tendons can become inflamed from repetitive motion of the shoulder. This can include overhead athletic activities such as swimming, tennis, or throwing. It can also occur from occupational activities such as painting or carpentry.
Patients may initially notice minor pain and a loss of strength. This, however, can progress into increasing discomfort with lifting the arm above the head, out to the side, or reaching behind the body.
Once impingement is diagnosed, the patient needs to avoid any painful activities or motions. Anti-inflammatory medications may be beneficial to decrease inflammation or swelling in the bursa or tendons. Rotator cuff strengthening exercises are crucial to successful treatment, as when the rotator cuff muscles are strong, bursitis and tendonitis is less likely to occur.
A cortisone injection, a direct acting anti-inflammatory, may be recommended to treat the
Impingement. The cortisone is injected into the subacromial bursa and acts by decreasing inflammation and increasing blood flow to the area which aids in healing.
If nonsurgical treatment fails arthroscopic surgery can help. Arthroscopy will remove any bone spurs, open the space above the rotator cuff, and remove the enlarged bursa. Surgery is an outpatient procedure that takes about 30 minutes. Rehabilitation time is 3-6 weeks. Patients wear a light sling after surgery for the first few days for comfort as needed.
Please watch the Surgical Videos