

There are two menisci in each knee. The meniscus on the inside of the knee is medial meniscus and the outside of the knee is called lateral meniscus. The meniscal cartilages are shaped like crescent moons and sit between the two bones that form the knee, the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shin bone). The menisci function primarily as shock absorbers and secondarily as stabilizers in the knee. The medial meniscus absorbs 30% of the load in the medial compartment and the lateral meniscus absorbs 50% of the load in the lateral compartment.
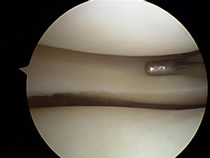
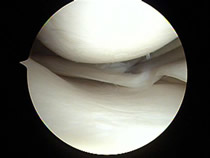
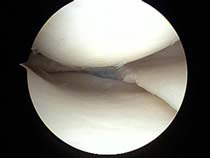
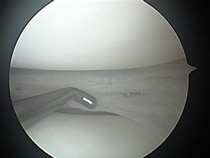
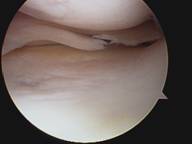
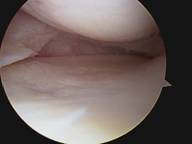
The menisci commonly tear when they are caught between the moving bones of the femur and tibia. The menisci have blood supply only to the outer 1/3 peripheral zone, and therefore have a limited ability to heal if torn. Most tears occur in the inner zones of the meniscus because this is the part of the meniscus that gets caught between the moving bones. These inner tears and many of the complex outer zone tears cannot heal.
Usually the exact cause of a meniscal tear is unknown making it difficult to prevent. The most severe damage to a meniscus usually occurs when a patient has an unstable knee with an untreated anterior cruciate ligament tear.
Pain is the most common symptom of a meniscal tear. The pain is usually located on the sides or behind the knee. Catching and occasionally locking also can occur. Swelling always means there is something wrong inside the knee and is commonly associated with meniscal tears.
The majority of a menicus does not have a blood supply and thus is not able to heal itself if torn. Over time the tear will remain and may progressively get larger and if mobile it may cause damage to the surface cartilage above and below the meniscus. Therefore very rarely is nonsurgical treatment for a meniscal tear recommended.
When the meniscus tears, the torn piece no longer has the capability to cushion the bone surfaces. If left alone the torn meniscal piece continues to tear into previously normal cartilage. As a result more meniscus is subsequently lost. In addition, in those meniscal tears that are reparable (longitudinal tears in the outer third) the tears will become unreparable because of additional damage to the meniscus. MRIscans are usually diagnostic of meniscal tears with an accuracy of aproximately 90%.
Arthroscopy of the knee is the recommended treatment for meniscal tears. Arthroscopy is a relatively simple surgical procedure that takes approximately 15 minutes. The procedure is done in a surgical center as an outpatient procedure. It can be done under local anesthesia through 2 portals or skin incisions 6mm wide (1/4 inch). After the procedure Band-aids are used to close the skin. Crutches usually are not necessary unless a repair of some other procedure is performed.
Please watch the Surgical Video.
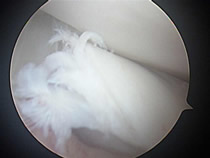
Following a partial menisectomy most patients are able to resume to normal non-sporting activities comfortably in a few days. Generally light sports such as biking and swimming are well tolerated in 1-2 weeks. Heavy sports such as running, basketball and tennis usually take longer.
The long-term prognosis depends on how much meniscus was lost from the tear. Naturally occurring (aging) arthritis is accelerated depending on the amount of meniscus lost. There are new techniques designed to repair those menisci that are reparable and replace that portion of the meniscus which is lost. Entire menisci can be replaced using cadaver transplants.
After a knee arthroscopy patients are instructed on knee range of motion and strengthening exercise. See knee rehabilitation brochure. Progression of activities is based on signs of swelling in the knee and pain.